The renminbi (RMB) has made significant progress towards internationalisation over the past decade, driven by China's economic strength and strategic initiatives. Key developments include the establishment of the Cross-Border Interbank Payment System (CIPS) for RMB transactions and the growing role of offshore RMB hubs like London. The potential of the digital RMB for cross-border payments could further strengthen the RMB’s long-term prospects for greater global use.
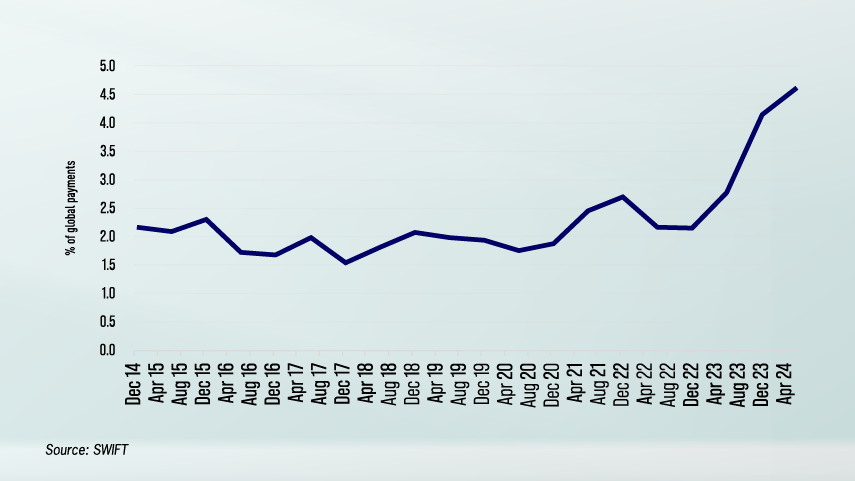
According to SWIFT, the RMB’s share of global payments rose to 4.7% in August 2024, reflecting its growing appeal, particularly in emerging markets. Though still behind dominant currencies like the United States (US) dollar and the euro, this growth is particularly notable in emerging markets, where countries facing currency volatility are turning to the RMB as a more stable alternative.
The RMB's role in global trade and finance is expanding, with the use of RMB settlement in China’s cross-border transactions with the world accounting for over 50% as of July 2023, up from 40% in 2019. Cross-border RMB payments reached RMB 52.3 trillion ($7.4 trillion) in 2023, driven by currency swap agreements with BRICS and Belt and Road Initiative countries. The RMB is increasingly used in central bank reserves, reaching $245.2 billion by the second quarter of 2024, and in global financial markets through Bond Connect and Stock Connect. Offshore RMB markets in Hong Kong, London, and Singapore support its growth. However, challenges remain, including capital controls, limited convertibility, and geopolitical factors.
For international financial institutions (FIs), Chinese and overseas companies, these dynamics present both opportunities and complexities as the global currency landscape shifts. Engagement with RMB-denominated assets and participation in RMB-based transactions could offer diversification benefits and access to China's vast market. But it also poses significant challenges due to regulatory complexities, currency volatility, and potential geopolitical risks that require careful management and strategic planning.
This year's survey results indicate that the RMB usage in cross-border trade settlement and trade financing remains high. Continuing last year's trend in 2023, the use of RMB for cross-border cash management among Chinese and overseas companies, as well as FIs, continues to experience rapid growth. Additionally, global FIs have significantly increased their use of RMB for cross-border investments and financing compared to last year's results, with the shares of cross-border RMB bonds, stocks, and direct investments increasing by 11, 14, and eight percentage points, respectively.
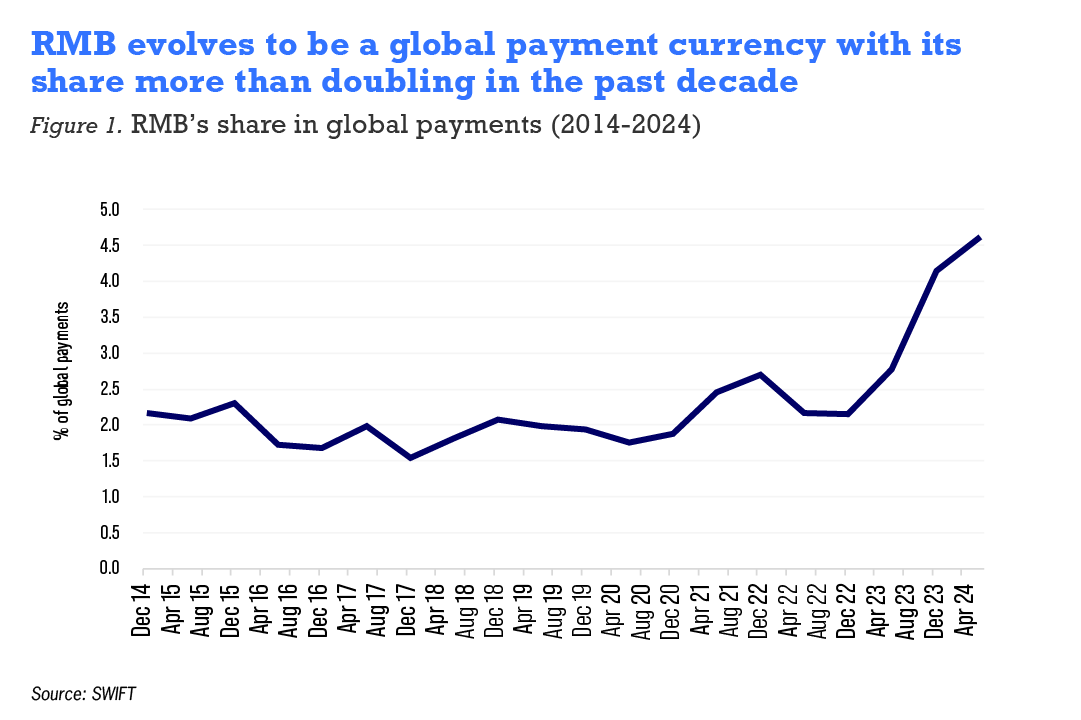
Europe, particularly the United Kingdom (UK), saw the most significant growth in RMB activities, with Chinese companies using RMB for cross-border trade settlement in the UK growing nearly fivefold from the previous year. While 43% of total financial institutions and 53% Chinese companies continue to regard geopolitical tension as a key challenge a notable decrease from last year's survey results of 62% and 74% respectively.
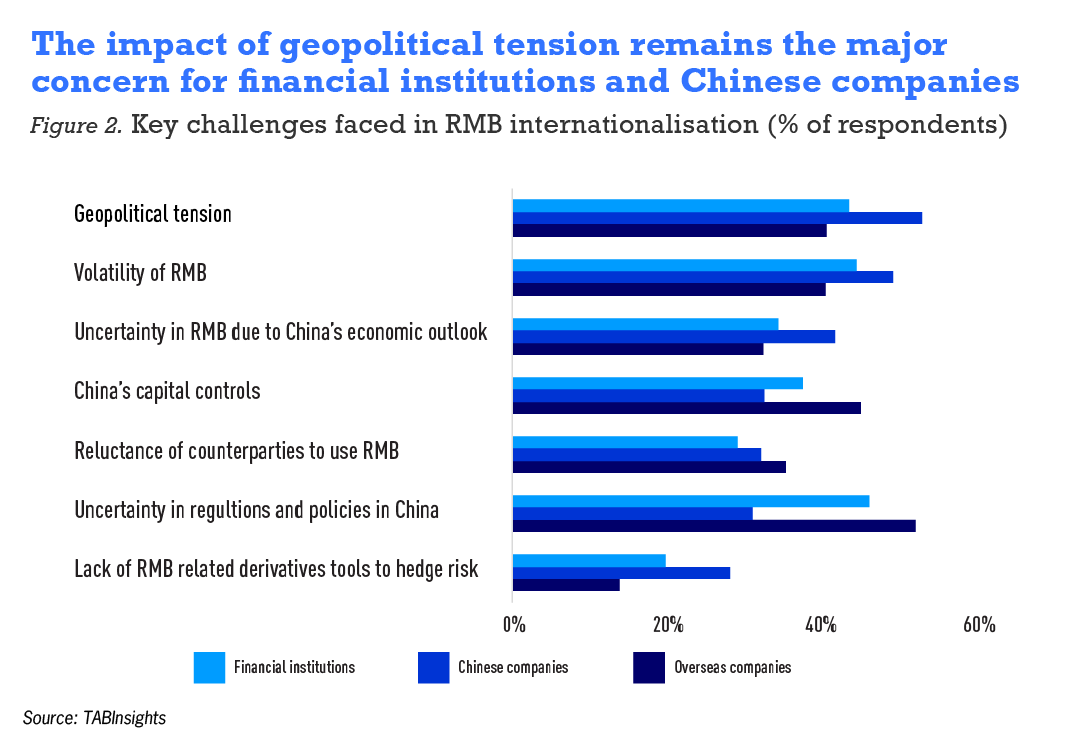
The use of RMB-based cross-border products has seen growth across various sectors in 2023
For Chinese companies, RMB cross-border trade settlement, cash management, and trade financing were the most widely used products, with usage rates of 78%, 51%, and 50%, respectively. Among all products, cross-border RMB stock investment and offshore RMB financing grew the fastest, both increasing by nine percentage points from the previous year’s survey results. Other RMB products also saw varying degrees of growth.
For overseas companies, RMB cross-border cash management became the most widely used product, surpassing cross-border RMB trade settlement, with a usage rate of 64%, up nine percentage points from the previous year’s survey results. The use of RMB cross-border investment and financing by overseas companies grew significantly, with the proportion of cross-border RMB bond and stock investments rising from 51% and 41% in last year’s survey to 61% and 52% this year.
Offshore RMB financing and wealth management also grew significantly, increasing by 13 and 14 percentage points, respectively, making them the fastest-growing RMB products. The only slight decline compared to last year’s survey results was in the use of RMB cross-border trade financing, which fell from 50% last year to 47% this year.
For FIs, the most widely used RMB products were RMB cross-border trade settlement and cash management. In 2023, FIs actively promoted RMB cross-border cash management products, with the usage rate increasing by 12 percentage points to 65%. The fastest-growing products were cross-border RMB stock investment and offshore RMB financing, with usage rates rising from 35% and 33% in last year’s survey to 49% and 47% this year. The usage of other RMB products remained largely consistent with last year’s results.
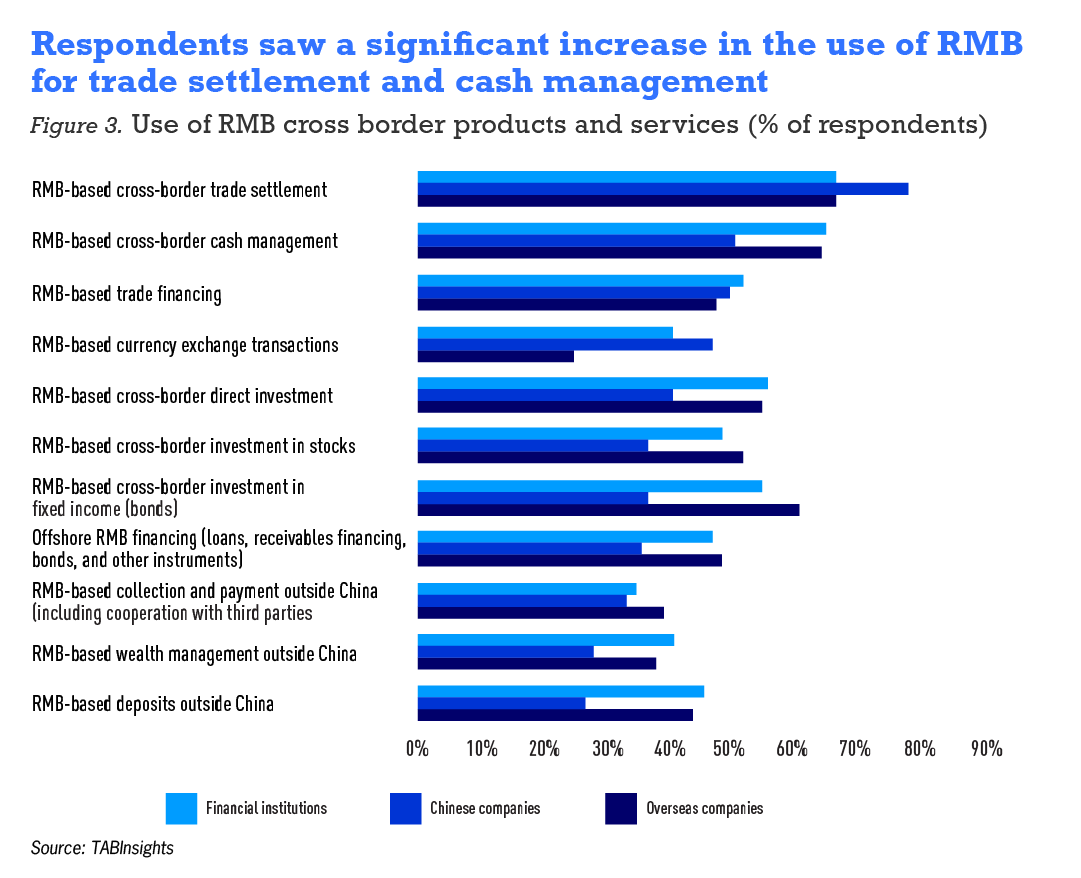
Changes in the destinations for cross-border direct investment by Chinese and overseas companies were observed this year, with strong growth in the EU and the UK
Sixteen percent and 22% of Chinese companies chose the European Union (EU) and the UK as investment destinations, up from 12% and 5% in last year’s survey, respectively. Thirty-five percent of overseas companies selected China as their preferred market for RMB investment, remaining unchanged from last year’s results. This year, the UK became a popular destination for overseas companies, increasing significantly from 5% to 19%.
China continues to promote the opening of its financial markets, attracting global investors
Key developments included enhancing the Panda bond framework, expanding the Stock Connect programme, and facilitating dual listings. These measures bolstered China’s position as the second-largest financial market globally. By the end of 2023, foreign investors held RMB 3.7 trillion ($521 billion) in Chinese bonds and RMB 2.8 trillion ($ 394 billion) in Chinese equities. Financial institutions demonstrated increased confidence in RMB-denominated assets, particularly bonds and stocks, with many significantly increasing their portfolio allocations. Over 50% of FIs planned to further increase their exposure to RMB bonds and China A shares in 2024.
This year’s survey shows an increase in RMB cross-border financing among FIs, with 45% of overseas FIs reporting that RMB financing accounted for 10% to 30% of their total financing. Chinese companies and overseas companies used RMB more frequently in accounts receivable financing, with bond issuance and bank loans being the most commonly used financing tools.
Geographically, China remains the most important market for RMB cross-border financing, with 27% of FIs stating that China is their primary market for RMB cross-border financing, up from 17% in last year’s survey. In 2023, RMB cross-border financing grew rapidly in the UK, while traditional markets such as East Asia (including Hong Kong, Macau, and Taiwan), South and Southeast Asia, and the EU remained stable compared to the previous year.
For RMB foreign exchange transactions, 88% of overseas companies, 73% of Chinese companies, and 77% of FIs reported that they increased or maintained their use of RMB in foreign exchange transactions, up by one, four, and two percentage points from the previous year’s results, respectively.
Development of the offshore RMB market and trading centres
In 2023, the offshore RMB market experienced notable shifts, with Chinese and overseas companies, as well as FIs, showing increased adoption in several regions. East Asia remains the primary region for RMB cross-border transactions.
Europe, particularly the UK, saw the most significant growth in RMB activities, with Chinese companies using RMB for cross-border trade settlement in the UK grew nearly fivefold from the previous year, and 67% choosing the UK for offshore RMB wealth management, up from 19% in the previous year’s survey. In contrast, RMB usage by Chinese companies in Central Asia, the Middle East, and Africa declined.
Overseas companies saw significant increases in RMB bond investment, cross-border cash management and direct investment in East Asia; in Europe, especially the UK, the use of RMB by overseas companies also increased notably.
Financial institutions also increased their use of RMB significantly, particularly in East Asia and Europe, including the UK, with RMB cross-border cash management and foreign exchange transactions rising significantly in these two regions.
In 2023, offshore RMB deposits remained largely stable across different respondents, with 46% of overseas companies reporting an increase in offshore RMB deposits. Chinese companies and FIs were more optimistic about 2024, expecting further growth in offshore RMB deposits.
Hong Kong remains the primary offshore RMB centre for cross-border transactions, with 36% of overseas companies, 42% of Chinese companies, and 37% of FIs choosing Hong Kong as their first choice. The proportion choosing the UK as a trading centre increased significantly compared to last year’s result, followed by Singapore.
The UK is playing an increasingly important role in the RMB financial market
This year marks the 10th anniversary of the PBOC authorising a RMB clearing bank in the UK. Since 2014, London has solidified its position as a global hub for RMB transactions, facilitating increased cross-border use of the RMB and supporting the development of the offshore RMB market.
In 2023, cross-border trade settlement between the two countries increased to RMB 3 trillion ($423 billion), a year-on-year increase of 22%. The volume of RMB payments and settlements in the UK reached a record high, with over RMB 20 trillion ($2.8 trillion) processed through the UK’s RMB clearing bank. The London Stock Exchange (LSE) played a critical role in RMB bond issuance, with RMB 31.2 billion ($4.4 billion) in new bonds issued, positioning the UK as a major international RMB bond market.
Survey results show that China-UK related respondents exhibited a diverse range of uses for RMB cross-border products. While their participation in RMB cross-border trade settlement was slightly lower than the overall survey level, they had higher participation in offshore RMB financing, cross-border investment, and foreign exchange transactions.
China-UK related Chinese companies showed significantly higher participation in cross-border investment and financing activities and RMB foreign exchange transactions than the overall level. Forty-six percent of companies participated in RMB cross-border bond and stock investment, 45% in offshore RMB financing, and 54% in foreign exchange transactions, all exceeding the overall level. China-UK related overseas companies had higher participation in offshore RMB financing and wealth management compared to the overall level.
FTA, local currency settlement, and capital market liberalisation are key factors influencing RMB internationalisation
In this year’s survey, the continued growth in the international use of RMB was driven by multiple factors. Surveyed institutions identified free trade agreements (FTA), particularly the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP), as key drivers, with 60% of Chinese companies and 64% of overseas companies selecting this factor.
The RMB’s global transaction share reached 4.7% in 2024, with emerging markets and BRICS nations increasingly favouring it as an alternative to the US dollar. RMB usage in cross-border trade has soared, making up over half of China's cross-border payments and facilitated by China’s extensive currency swap agreements. In finance, the RMB is increasingly held in reserves by BRICS central banks, and RMB-denominated assets have gained traction through the Bond and Stock Connect initiatives.
Capital market liberalisation, including enhancements to the Panda bond framework, is expected to boost RMB-based product adoption. Additionally, the introduction of RMB bank card clearing for Mastercard and AMEX is anticipated to increase usage, with 59% of overseas companies and 52% FIs planning greater engagement.
Eighty-eight percent of overseas companies and 74% of FIs showed greater readiness to use the digital RMB (e-CNY), while Chinese companies were more cautious, with 52% of Chinese companies expressing willingness to use it.
The RMB’s journey towards internationalisation has accelerated, supported by China’s long term economic strength and initiatives like CIPS and currency swap agreements with BRICS and BRI nations. While RMB-denominated assets and reserves are growing, challenges remain, including capital controls, limited convertibility, and geopolitical dynamics favouring the US dollar. For international Fis and companies, RMB integration offers diversification opportunities but demands careful navigation of regulatory and geopolitical complexities as the RMB’s influence in global finance gradually expands.
Download the full RMB Internationalisation Report 2024 at https://reports.tabinsights.com/reports/rmb-internationalisation-report-2024
Survey methodology
The seventh edition of the global RMB Internationalisation Survey, conducted by China Construction Bank and The Asian Banker, evaluates RMB usage in cross-border trade, payments, investment, and financing. The survey, conducted between July and August 2024, included 2,487 senior executives from financial institutions, Chinese companies, and overseas companies across 23 global markets.
The survey sampled 1,134 Chinese companies, and 943 overseas companies (from North and South America, Europe, Asia Pacific, the Middle East, and Africa).
It also surveyed 250 financial institutions (FIs) from China and 160 FIs from outside China, which are engaged in cross-border business with China. Those represent larger financial institutions including banks, insurances and asset management companies.
Respondents were senior finance professionals—chief financial officers, corporate treasurers, and senior finance managers—focused on RMB products or financing and were tasked to complete an online questionnaire.